Navigating the Sarkari Exam Maze: A Qualification-Wise Guide to Your Dream Government Job
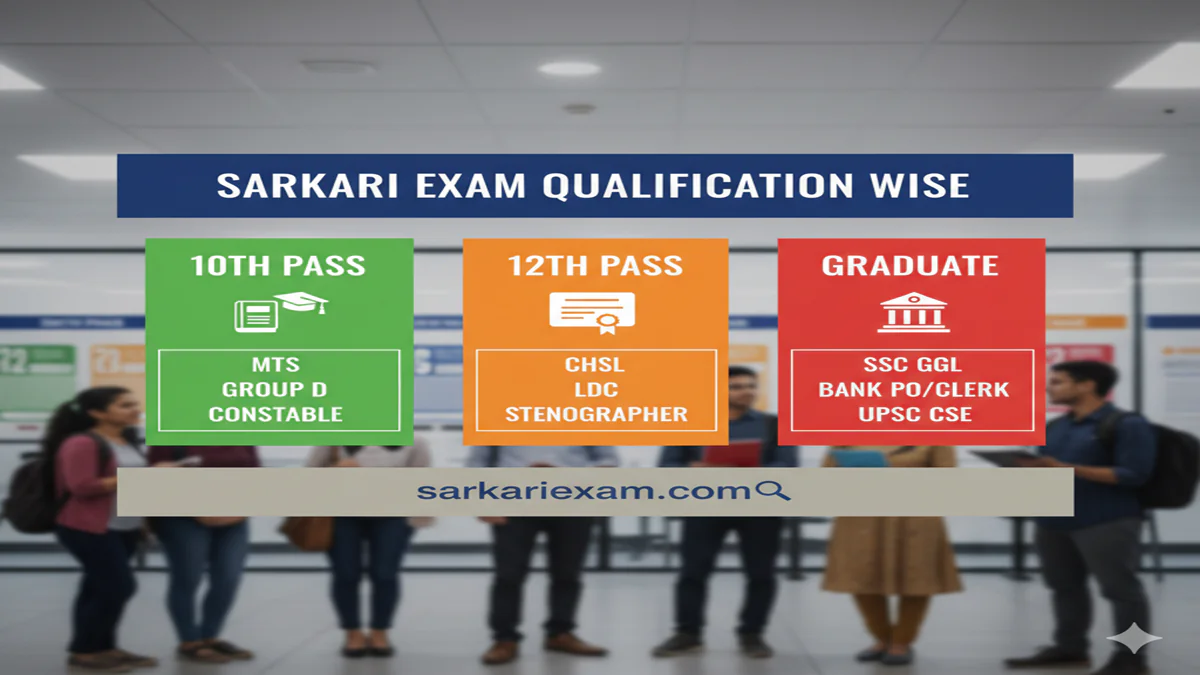
Sarkari Exam Qualification Wise In India, the term “Sarkari Naukri” (Government Job) symbolizes more than just employment; it represents stability, respect, social security, and a chance to contribute to the nation’s machinery. However, the path to securing such a position is through a highly competitive and structured labyrinth of examinations. With over 50+ recruiting agencies like UPSC, SSC, RBI, and numerous state-level boards, aspirants often find themselves confused about which exams they are eligible for based on their educational qualifications.
This guide demystifies the Sarkari exam ecosystem by categorizing it qualification-wise. Whether you are a fresh 10th pass, a graduate, or a post-graduate, understanding this map is the first strategic step in your preparation journey.
The Foundation: Understanding the Exam Tiers
Most government exams are conducted in multiple tiers:
- Tier-I:Preliminary exam, usually objective, used as a screening test.
- Tier-II:Mains exam, can be objective or descriptive, testing in-depth knowledge.
- Tier-III:Personal Interview or Skill Test (like typing for clerks, computer proficiency).
- Tier-IV:Document verification and medical examination.
Now, let’s break down the exams based on the minimum educational qualification required.
1. For 10th Pass (Matriculate) Candidates
This is the entry point into the government sector. Jobs at this level are primarily in Group C and D, offering a stable career right after school.
Popular Job Profiles: Constable, Forest Guard, Peon/Chaprasi, Multi-Tasking Staff (MTS), Postal Assistant, Lower Division Clerk (LDC) in some states.
Key Examinations:
- SSC Multi-Tasking Staff (MTS):One of the most popular exams for 10th pass candidates. It recruits for various ministerial and support roles in different government offices.
- SSC GD Constable:For recruitment of General Duty Constables in CAPFs, SSF, and Rifleman in Assam Rifles.
- Railway Recruitment Board (RRB) Group D (now Level-1):Recruits for roles like Track Maintainer, Helper, Porter, etc., in Indian Railways.
- State Police Constable Exams:Each state conducts its own constable recruitment drives (e.g., UPPCP, Maharashtra Police, MP Police).
- Indian Army Soldier GD/Technical/Nursing Assistant:Various recruitment rallies are held for 10th/10+2 pass candidates.
Preparation Focus: Emphasis on basic Mathematics, General Intelligence & Reasoning, General Awareness (simple science, history, geography), and Basic Language skills. Physical Standard Test (PST) and Physical Efficiency Test (PET) are crucial for police and paramilitary roles.
2. For 10+2 (Intermediate) Pass Candidates
A 12th-class certificate opens a wider array of opportunities, especially in technical, non-gazetted, and clerical fields.
Popular Job Profiles: Clerk, Stenographer, Tax Assistant, Junior Accountant, Railway Ticket Collector, Armed Forces (NDA, Air Force/Navy Agniveer), Secretariat Assistant.
Key Examinations:
- SSC Combined Higher Secondary Level (CHSL):The premier exam for 10+2 pass candidates to secure posts like Lower Division Clerk (LDC), Data Entry Operator (DEO), and Court Clerk.
- Railway Recruitment Board (RRB) NTPC (Graduate & Undergraduate Posts):While many posts require graduation, several like Clerk, Typist, and Station Master are open to 12th pass candidates.
- National Defence Academy (NDA):Conducted by UPSC for entry into the Army, Navy, and Air Force wings after 12th (with Physics & Maths for Air Force/Navy).
- Agniveer (All three services):The new tour-of-duty scheme for recruitment into the armed forces.
- State-level Clerical Exams:Each state’s Public Service Commission conducts clerical cadre exams (e.g., MPESB, Kerala PSC LDC).
Preparation Focus: The syllabus deepens. Quantitative Aptitude, Advanced Reasoning, General Awareness (current affairs, static GK), and English/Hindi language comprehension become critical. For technical roles in railways or defense, subject-specific knowledge (Physics, Maths) is tested.
3. For Graduate Candidates (The Vast Arena)
This is the most expansive and competitive category. A bachelor’s degree in any discipline (Arts, Science, Commerce) is the gateway to the majority of prestigious Sarkari exams.
Popular Job Profiles: Probationary Officer (PO), Clerk in Banks, Sub-Inspector (CBI/Police), Income Tax Inspector, Excise Inspector, Section Officer, Assistant in various ministries, Teacher (TGT).
Key Examinations:
- Banking Sector:
- IBPS PO/IBPS Clerk:The flagship exams for public sector bank Probationary Officers and Clerical staff.
- SBI PO/SBI Clerk:Separate, highly competitive exams for the country’s largest bank.
- RBI Assistant/Office Attendant:For roles in the Reserve Bank of India.
- Staff Selection Commission (SSC):
- SSC Combined Graduate Level (CGL):The “king” of graduate-level exams, offering prestigious posts like Income Tax Inspector, CBI Sub-Inspector, Auditor, and Assistant Section Officer.
- SSC CPO (Central Police Organisation):For recruitment of Sub-Inspectors in Delhi Police and CAPFs.
- SSC Selection Post (Phase X/XI):For graduate-level posts in various departments.
- Defence & Police:
- CDS (Combined Defence Services):UPSC-conducted exam for entry into Indian Military Academy, Officers Training Academy, Air Force Academy, and Naval Academy for graduates.
- AFCAT (Air Force Common Admission Test):For graduate men and women to join the Flying, Technical, and Ground Duty branches of the IAF.
- Railways:
- RRB NTPC (Graduate Posts):For commercial apprentice, traffic apprentice, goods guard, etc.
- State-Level Exams:
- State PSC Upper Subordinate Services (Like UPPSC PCS):For Deputy Collector, DSP, BDO, and other state civil services (often requires graduation).
- State Police SI Exams:For Sub-Inspector roles in state police forces.
Preparation Focus: Graduate-level exams demand a strategic approach. The syllabus includes High-Level Quantitative Aptitude & Data Interpretation, Advanced Reasoning, Comprehensive General Awareness (current affairs, polity, economy, geography, science), and a strong command over English (comprehension, grammar, vocabulary). Subject-specific optional papers may appear in Tier-II of exams like SSC CGL.
4. For Engineering Graduates (B.Tech/B.E.)
Engineers have dedicated entry routes into prestigious technical and managerial services, often with higher starting salaries.
Popular Job Profiles: Engineer (Civil, Mechanical, Electrical, Electronics) in PSUs, Indian Engineering Services (IES) Officers, Software Engineers in ISRO/DRDO, Technical Officers.
Key Examinations:
- UPSC Engineering Services Examination (ESE):The most prestigious exam for engineers, leading to appointments in Indian Railway Service of Engineers, Central Engineering Service, etc.
- GATE (Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering):Primarily forM.Techadmissions, but scores are extensively used for recruitment inPublic Sector Undertakings (PSUs)like ONGC, BHEL, NTPC, Power Grid, IOCL, etc. (Recruitment through GATE).
- ISRO/DRDO Scientist/Engineer Recruitment:Direct recruitment drives or exams for research and technical roles.
- SSC JE (Junior Engineer):Conducted by SSC for JE posts in Civil, Mechanical, Electrical, and Quantity Surveying & Contracts departments.
- RRB JE (Junior Engineer):For JE posts in Indian Railways.
- State PSC Assistant Engineer (AE) Exams:For state government engineering departments (Irrigation, PWD, etc.).
Preparation Focus: Core engineering subject knowledge is paramount, especially for ESE and GATE. Alongside technical prowess, exams like ESE also test General Studies and English. For PSUs via GATE, the GATE score is primary, often followed by an interview.
5. For Post-Graduate & Specialized Degree Holders
A master’s degree or specialized professional qualification (MBA, CA, Law) opens doors to highly specialized, advisory, and high-ranking positions.
Popular Job Profiles: Officers in RBI/SEBI/NABARD, Economists, Statisticians, Law Officers, Managers, Assistant Professors, Scientists.
Key Examinations:
- UPSC Civil Services Examination (CSE):The apex exam. While graduates can appear, post-graduates often have a subject-depth advantage. Leads to IAS, IPS, IFS, etc.
- RBI Grade B Officer:One of the most sought-after jobs in the finance sector, requiring deep economic and financial knowledge.
- SEBI Grade A Officer:For roles in the Securities and Exchange Board.
- NABARD Grade A & B:For development and managerial roles in rural banking.
- CSIR NET (For Science Subjects):For lectureship and JRF in sciences.
- SSC Combined Higher Secondary Level (CHSL):(For some specialized posts) andSSC CGL(for posts like Statistical Investigator, which requires a Statistics background).
- State PSC Combined State Service Exam:For state civil services, where a post-graduate degree can be beneficial.
Preparation Focus: The preparation becomes highly specialized. For regulatory bodies (RBI, SEBI), in-depth knowledge of finance, economics, and management is tested. For teaching exams (NET), mastery over the chosen subject is critical. For CSE, a vast, interdisciplinary understanding of national and international issues is required.
Strategic Roadmap for Aspirants
- Self-Assessment:Honestly evaluate your qualification, interests, and strengths. Are you strong in aptitude, your core subject, or general awareness?
- Goal Identification:Match your profile to the job roles and exams listed above. Don’t just follow the crowd; choose a path that aligns with your degree.
- Notification Awareness:Regularly visit official websites (UPSC, SSC, RRB, State PSCs) and follow reputable job portals for exact eligibility details (age limit, percentage criteria, subject specifications).
- Structured Preparation:Once the target is set, create a study plan covering the entire syllabus, giving weightage to your strong and weak areas.
- Consistency & Revision:Regular study and revision of current affairs and core concepts are non-negotiable.
- Practice is Key:Solve previous years’ question papers and take mock tests to build speed, accuracy, and exam temperament.
Conclusion
The world of Sarkari exams is vast but not unnavigable. By clearly understanding the opportunities available at your educational level, you can channel your efforts efficiently and avoid dissipating energy on irrelevant exams. Remember, the right qualification is your key to unlock a specific door in this vast corridor. Choose your door, prepare your key with dedication, and persevere. Your Sarkari Naukri awaits.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: I am a final year graduate student. Can I apply for graduate-level exams like SSC CGL or IBPS PO?
Ans: Yes, absolutely. Most government exams allow final year students to apply, provided you can submit proof of passing the required qualification (degree certificate) by a specified date mentioned in the official notification. This date is usually before the document verification stage.
Q2: Is there any advantage to having a post-graduate degree when applying for exams that only require graduation (like UPSC CSE or SSC CGL)?
Ans: While having a PG degree doesn’t grant extra marks directly in most exams, it offers significant indirect advantages. It provides deeper subject knowledge, which can be beneficial for the Mains (descriptive) stage of UPSC or for specific optional subjects. It also indicates a higher level of academic maturity. However, for objective-type exams like SSC CGL, the advantage is minimal beyond potentially better comprehension skills.
Q3: I am a B.Com graduate. Am I eligible for technical exams like RRB JE or SSC JE?
Ans: No. Exams for Junior Engineer (JE) posts have strict educational eligibility criteria requiring a diploma or degree in the specific engineering discipline (Civil, Mechanical, Electrical, etc.). A B.Com graduate is not eligible. However, you are highly eligible for accounts, auditor, and tax assistant roles in SSC CGL, or for banking exams.
Q4: Are there any government exams for which a PhD is required or beneficial?
Ans: Direct exams specifically requiring a PhD are rare. However, a PhD is highly beneficial and sometimes preferred for:
- Research Scientist positionsin organizations like DRDO, ISRO, ICMR, BARC, where recruitment is done through specialized notifications.
- Teaching positionsin central universities, where it is now mandatory (as per UGC regulations) in many cases.
- Thehighly specialized “Direct Recruitment”posts (like Economists, Statisticians) in ministries and regulatory bodies often seek doctoral-level expertise.
Q5: How important is the percentage/CGPA in my degree for Sarkari exam eligibility?
Ans: This varies significantly:
- Most exams (SSC, Banking, Railway):Only require thepassing percentage(usually 50-60% for general, with relaxations for reserved categories) as per your university norms. A higher percentage does not affect your selection score unless specified.
- UPSC Civil Services & others:Only apass certificateis required. Your marks in graduation do not influence your score.
- State-level Exams:Some state commissions may have specific percentage requirements.Always check the “Educational Qualification” section of the official notification meticulously.